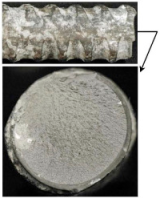
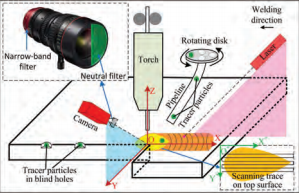
 A visionbased sensing system was improved to acquire 2D images of weld pool shape and tracer particle movement simultaneously. …..
A visionbased sensing system was improved to acquire 2D images of weld pool shape and tracer particle movement simultaneously. …..
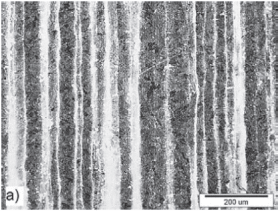
Based on analysis of tracer particle movement, roles of different associated forces, such as gravity, arc drag force, Maragoni force, magnetic force, droplet impact, and viscous force, were investigated. The results show that liquid metal under the arc decreases to a thin liquid layer if the welding speed is more than 1.0 m/min. This phenomenon makes viscous resistance increase in the thin liquid layer, which impedes transverse spreading of liquid metal. Thus, it is difficult for the weld toe to be filled by molten metal. Meanwhile, experiments revealed the amount of forward molten metal can be ignored in the front and middle of the weld pool. Therefore, it is difficult for the weld toe to be filled by the backward molten metal. As a result, undercutting defects appear during highspeed welding……..