A thesis published by Conerstone : A Collection of Scholarly and Creative Works for Minnesota State University, Mankato.
Additive manufacturing (AM) also known as 3D printing has tremendous advancements in récent days with a vast number of applications in industrial, automotive, architecture, consumer projects, fashion, toys, food, art, etc. Composite materials are widely used in structures with weight as a critical factor especially in aerospace industry. Recently, additive manufacturing technology, a rapidly growing innovative technology, has gained lot of importance in making composite materials. The properties of composite materials depend upon the properties of constituent’s matrix and fiber. There is lot of research on effect of fiber orientation on mechanical properties of composite materials made using conventional manufacturing methods. It will be interesting and relevant to study the relationship between the fiber orientation and fiber volume with mechanical properties of additively manufactured composite materials. This thesis work presents experimental investigation of mechanical behavior like tensile strength and fatigue life with variation in fiber orientation and fiber volume fraction of 3D printed composite materials. The aim is to study the best combination of volume fraction of fiber and fiber orientation that has better fatigue strength for additive manufactured composite materials. Using this study, they can decide the type of orientation and volume percent for desired properties. This study also finds the range of fatigue limits of 3d printed composite materials .
Read more
WordPress:
J'aime chargement…
 Le centre associé au Cetim dans le Grand-Est souffle ses 40 bougies le 6 octobre 2017 à Mulhouse. L’occasion pour les participants de découvrir ses installations, ses savoir-faire et d’inaugurer sa nouvelle plateforme d’expérimentation R&D et de démonstration « matériaux composites et recyclage ».
Le centre associé au Cetim dans le Grand-Est souffle ses 40 bougies le 6 octobre 2017 à Mulhouse. L’occasion pour les participants de découvrir ses installations, ses savoir-faire et d’inaugurer sa nouvelle plateforme d’expérimentation R&D et de démonstration « matériaux composites et recyclage ».
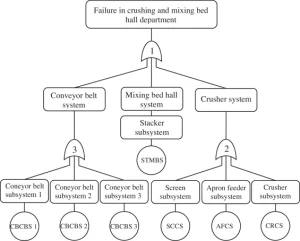
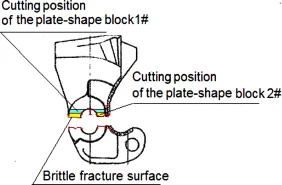




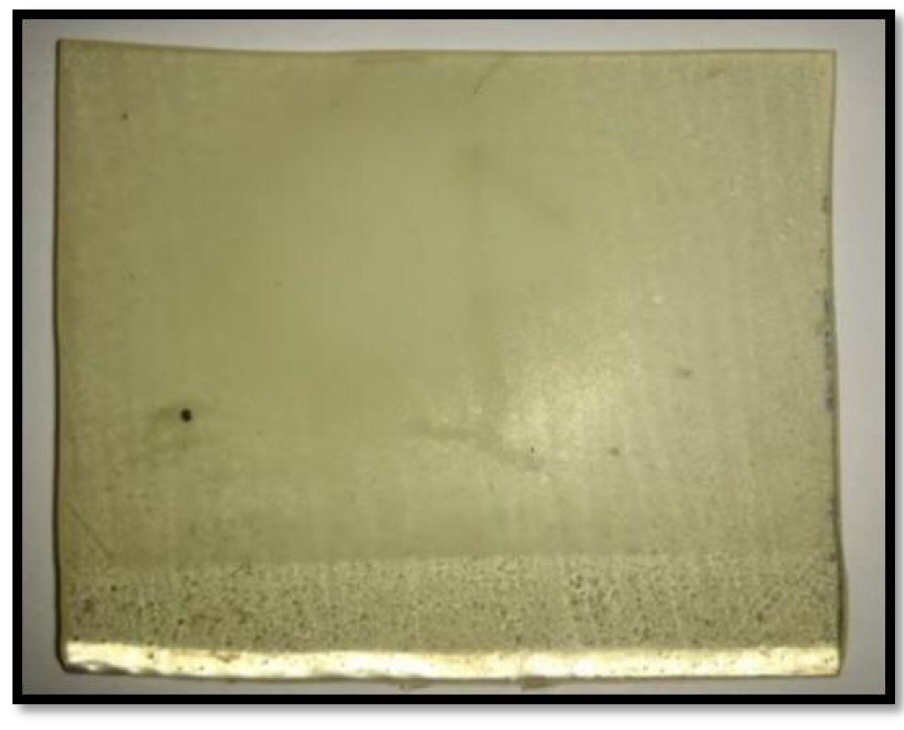 An article published on the JOURNAL OF THE EGYPTIAN SOCIETY OF TRIBOLOGY (VOLUME 14, No. 2, April 2017).
An article published on the JOURNAL OF THE EGYPTIAN SOCIETY OF TRIBOLOGY (VOLUME 14, No. 2, April 2017).