 An article published in « Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis« , 2014.
An article published in « Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis« , 2014.
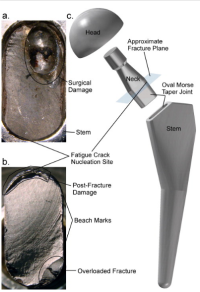
The tapered joints of modular hip implants are prone to fretting and crevice-corrosion. This can lead to total failure in under a year, especially for heavier, more active implant recipients. In this study, fractography of a failed Profemur Z implant showed that a life limiting fatigue crack was nucleated on the anterolateral surface of the implant’s neck. The fatigue crack nucleation area appeared to have both more fretting damage and a higher corrosion rate than on other surfaces of the neck.