 An article about a Case study of failure analysis published in « Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis« , July 2013.
An article about a Case study of failure analysis published in « Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis« , July 2013.
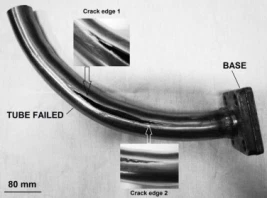
A high pressure oil tube with nominal diameter 50.8 mm and nominal thickness 4 mm has prematurely failed with a longitudinal crack. The failure was detected after 11 months of operation. The tube is part of the hydraulic power unit of an off shore oil and gas platform. The maximum designed internal pressure was 20 MPa and the service temperature was 25 °C with no significant variation. In practice, the internal pressure varies from 16 to 20 MPa under operation, and shutdowns rarely occur.

 A new interesting paper in
A new interesting paper in  Kiln of a lime plant, a part of an integrated steel plant, converts limestone (CaCO3) into lime (CaO) by heating at a temperature of around 900 °C using coke oven gas as a fuel. Coke oven gas is a by-product of the coke plant, which contains mainly hydro-carbons. The coke oven gas is lanced into the kiln through a number of pipes attached to the kiln. The lance pipes are cracking prematurely within 6 months of their service against an expected service life of 3 years. The analysis of cracking of the lance pipe is presented in this article. It will be published in
Kiln of a lime plant, a part of an integrated steel plant, converts limestone (CaCO3) into lime (CaO) by heating at a temperature of around 900 °C using coke oven gas as a fuel. Coke oven gas is a by-product of the coke plant, which contains mainly hydro-carbons. The coke oven gas is lanced into the kiln through a number of pipes attached to the kiln. The lance pipes are cracking prematurely within 6 months of their service against an expected service life of 3 years. The analysis of cracking of the lance pipe is presented in this article. It will be published in  High pressure pipe failed by fatigue in the fusion line of longitudinal weld.
High pressure pipe failed by fatigue in the fusion line of longitudinal weld.