 Le BEA fait appel aux experts Analyse de Défaillances du Cetim.
Le BEA fait appel aux experts Analyse de Défaillances du Cetim.
Archives du mot-clef Composites
EXPERIMENTAL AND NUMERICAL STUDY OF OBLIQUE IMPACT ON HELICOPTER BLADES
 A work presented on ECCM16 – 16TH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS, Seville, Spain, 22-26 June 2014
A work presented on ECCM16 – 16TH EUROPEAN CONFERENCE ON COMPOSITE MATERIALS, Seville, Spain, 22-26 June 2014
This work focuses on the study of medium velocity (~70 m/s) oblique impacts on the lower surface of helicopter blades. In this study, the influence of the local curvature of the blade on the response to an oblique impact is investigated. A numerical study is also performed. It is shown that for the geometries involved in the design of helicopter blades, the curvature does not have any influence on the structural response to an impact. However, in the case of oblique impacts, the curvature can change locally the impact angle so that the damage is different than for impacts on a planar sample.
Read more at : http://www.escm.eu.org/eccm16/assets/0339.pdf
Quand le BEA s’appuie sur les compétences du Cetim
 Erreur humaine ou défaillance technique ? Suite à un accident d’hélicoptère, le Bureau d’enquêtes et d’analyses (BEA) a fait appel à l’expertise du Cetim dans les matériaux composites. Sa mission : étudier les débris de la poutre de queue de l’appareil, afin de déterminer les causes exactes du sinistre. Découvrez en image cette enquête de haut vol sur notre site.
Erreur humaine ou défaillance technique ? Suite à un accident d’hélicoptère, le Bureau d’enquêtes et d’analyses (BEA) a fait appel à l’expertise du Cetim dans les matériaux composites. Sa mission : étudier les débris de la poutre de queue de l’appareil, afin de déterminer les causes exactes du sinistre. Découvrez en image cette enquête de haut vol sur notre site.
Pour en savoir plus, retrouvez les experts du Cetim sur le salon JEC World Composite Show & Conferences, du 8 au 10 Mars 2016 à Paris Nord Villepinte, Espace régional Pays de la Loire, stand 6P57. Vous pouvez également consulter le site du Cetim, rubrique « Agenda ».
Failure Analysis of HDPE Pipe for Drinking Water Distribution and Transmission
Un article paru dans la revue « Design and Modeling of Mechanical Systems » de mars 2015.
« Pipes and elbows are important components in any piping systems for transportation of water. These structures are subjected to complex loads taking into account their geometrical configuration and the multiplicity of the loading conditions in service. The origin of failure of these mechanical components is directly related to the presence of defects. The principal objective of this work is to analyze the severity of defects on high density poly-ethylene pipe widely used for water piping networks. »
Effect of Ply Orientation on Strength and Failure Mode of Pin Jointed Unidirectional Glass-epoxy Nanoclay Laminates
An article published in « Defence Science Journal « , November 2015. In this work the effect of the different ply orientations and nano filler on the bearing strength and failure mode of the pin joints is investigated both experimentally and numerically. Results show that the strength of the pin joints is drastically dependent on both ply orientations and nanofiller wt%. The joint geometry i.e., the distance from the free edge of specimen to the diameter of the hole (E/D) ratio and width of the specimen to the diameter of the holes (W/D) ratio were also investigated which effected the failure mode of the joints. Tsai-Wu failure theory along with the characteristics curve method was used for the prediction of failure modes numerically. Read more ….
« , November 2015. In this work the effect of the different ply orientations and nano filler on the bearing strength and failure mode of the pin joints is investigated both experimentally and numerically. Results show that the strength of the pin joints is drastically dependent on both ply orientations and nanofiller wt%. The joint geometry i.e., the distance from the free edge of specimen to the diameter of the hole (E/D) ratio and width of the specimen to the diameter of the holes (W/D) ratio were also investigated which effected the failure mode of the joints. Tsai-Wu failure theory along with the characteristics curve method was used for the prediction of failure modes numerically. Read more ….
Essais et analyses en fatigue et en rupture : données matériaux
 Que vous soyez au stade R&D (développement matériaux ou applicatif matériaux) ou au stade de production (contrôle qualité d’un composant mécanique, contrôle en cours de fabrication), vous souhaitez connaître ou vérifier les caractéristiques en fatigue et en rupture d’un matériau. Les équipes du Cetim vous proposent un accompagnement pour la réalisation de vos essais sur matériaux Métalliques, Composites et Elastomères.
Que vous soyez au stade R&D (développement matériaux ou applicatif matériaux) ou au stade de production (contrôle qualité d’un composant mécanique, contrôle en cours de fabrication), vous souhaitez connaître ou vérifier les caractéristiques en fatigue et en rupture d’un matériau. Les équipes du Cetim vous proposent un accompagnement pour la réalisation de vos essais sur matériaux Métalliques, Composites et Elastomères. 
Journal of the Indian Institute of Science A Multidisciplinary Reviews Journal
 A publication of the « Journal of the Indian Institute of Science » about nanocomposites.
A publication of the « Journal of the Indian Institute of Science » about nanocomposites.
Fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) composites are widely used in structural applications, mainly due to their high specific strength and stiffness. These composites experience several types of static and fatigue loads in service. For a safe and durable structure, high fracture toughness and enhanced fatigue life are prominent requirements of these composite materials. Efforts have been made in recent times to improve the fracture toughness and fatigue properties of FRP composites by incorporation of second phase fillers in the epoxy matrix. Addition of nano sized fillers to the epoxy has led to the development of a new class of materials— polymer nanocomposites. The presence of nano fillers has been shown to improve the fracture toughness and fatigue life of bulk epoxies as well as FRPs with nano-modified epoxy matrix. The type of nano filler, its shape, size, volume fraction and dispersion in the epoxy have all been shown to influence these properties significantly. In this review, an overview on the effect of nano fillers on the fracture toughness and fatigue life of bulk epoxies and FRPs is presented. The mechanisms proposed for observed improvements in these properties and the empirical method of prediction of fatigue life of nanocomposites subjected to spectrum fatigue loads simulating service loads are also discussed.
Failure Analysis of a Polymer Centrifugal Impeller
 An other new case study of failure analysis had been published in october 2015 in Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis.
An other new case study of failure analysis had been published in october 2015 in Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis.
A failure analysis investigation was performed on a fractured polymer impeller used in a respiratory blower. A radial split down the impeller center was observed, with symmetric fracture faces about the impeller bore. The brittle fracture morphology and defects within the impeller bore suggest that premature failure occurred because of multiple interacting factors including: intermittently high centrifugal velocities, imbalance bore and shaft conditions, defects within the bore caused by machining, and stress concentrations along the circumference of the impeller lip.
Read more at : Failure Analysis of a Polymer Centrifugal Impeller.
Failure Analysis of a Polymer Centrifugal Impeller
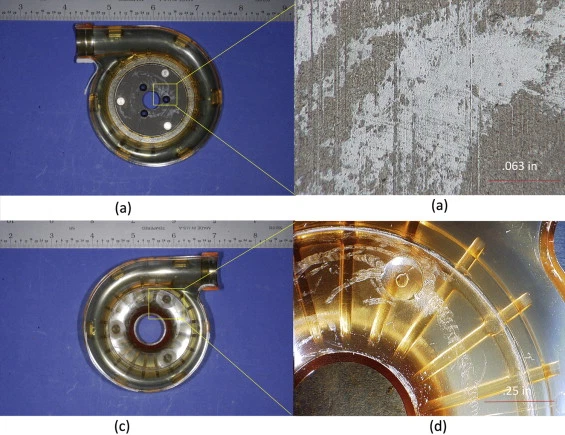 A new case study published in Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis and posted on Sciencedirect.com.
A new case study published in Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis and posted on Sciencedirect.com.
The failure analysis investigation was performed on a fractured polymer impeller used in a respiratory blower. The brittle fracture morphology and defects within the impeller bore suggest that premature failure occurred because of multiple interacting factors including: intermittently high centrifugal velocities, imbalance bore and shaft conditions, defects within the bore caused by machining, and stress concentrations along the circumference of the impeller lip.
more at : Failure Analysis of a Polymer Centrifugal Impeller.
Des défauts sous les flashs
 Le groupe Duqueine a adopté la thermographie infrarouge active afin de s’assurer de la qualité des composites utilisés pour un capot d’essai de réacteur d’avion. Les experts du Cetim, sollicités par l’entreprise, proposent alors d’optimiser le procédé de thermographie infrarouge active.
Le groupe Duqueine a adopté la thermographie infrarouge active afin de s’assurer de la qualité des composites utilisés pour un capot d’essai de réacteur d’avion. Les experts du Cetim, sollicités par l’entreprise, proposent alors d’optimiser le procédé de thermographie infrarouge active.
 Pour lire l’article cliquez ici
Pour lire l’article cliquez ici

