 An article published in « International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology« , January 2014.
An article published in « International Journal of Innovative Research in Science, Engineering and Technology« , January 2014.
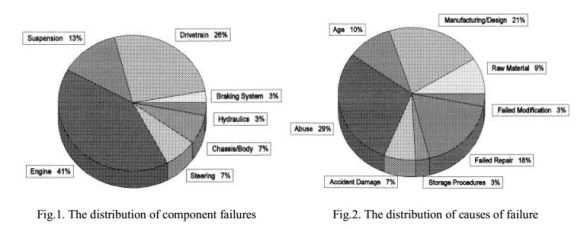
This paper presents an investigation report of effect of various parameters which affect the performance of an automobile engine. Almost all internal combustion engines have at least one connecting rod to transmit the thrust of the piston to the crankshaft, and as the result the reciprocating motion of the piston is translated into rotational motion of the crankshaft. From the viewpoint of functionality, connecting rods must have the highest possible rigidity at the lowest weight capable to withstand varying loads. It has been found that structural failure of various components results in engine missing and starts producing noise and vibration during racing, mileage gets affected and black or white smoke arise also pickup gets reduced. In automobile industry damaged or broken parts are generally too expensive to replace or repair especially in case of engine. In this concern they presented detailed analysis of causes along with preventive maintenance suggestion schedule for better engine life.

WordPress:
J'aime chargement…
 A new paper in « Case study in Engineering Failure Analysis » published on ScienceDirect.com.
A new paper in « Case study in Engineering Failure Analysis » published on ScienceDirect.com.

