 An article published in « Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis« , octobre 2014.
An article published in « Case Studies in Engineering Failure Analysis« , octobre 2014.
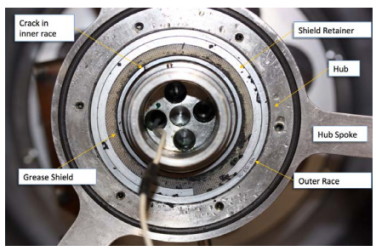
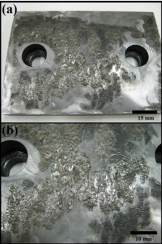
Journal bearings as so sensitive parts of steam turbines are very susceptible to failure through different mechanisms of wear, fatigue and crush during service conditions. Failure occurring through these mechanisms lead to turbine completely shut down as a result of interfering in working conditions of bearing different parts. In this paper, failed interfered part of a journal bearing related to a 320,000 kW steam turbine was examined. The studies were revealed that the bearing part loosing and inappropriate clearance can produce relative displacements under cyclic gradient loading. This condition was detrimental for the service life of turbine journal bearing via failure through fretting fatigue mechanism.