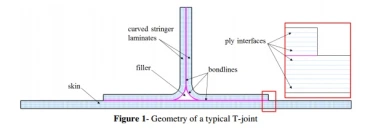
 A pubication in « Journal of Physics »: Conference Series, 2014. Wind turbine industry utilizes composite materials in turbine blade structural designs because of their high strength/stiffness to weight ratio. T-joint is one of the design configurations of composite wind turbine blades. T-joints are prone to delaminations between skin/stiffener plies and debonds between skin-stiffener-filler interfaces. In this study, delamination/debond behavior of a co-bonded composite T-joint is investigated under 0° pull load condition by 2D finite element method. The failure sequence consists of debonding of filler/stringer interface during one load drop followed by a second drop in which the 2nd filler/stringer debonds, filler/skin debonding and skin delamination leading to total loss of load carrying capacity. This type of failure initiation has been observed widely in the literature. Failure initiation and propagation behavior, initial and max failure loads and stress fields are affected by the property change. In all cases mixed-mode crack tip loading is observed in the failure initiation and propagation stages. In this paper, the detailed delamination/debonding history in T-joints is predicted with cohesive elements for the first time.
A pubication in « Journal of Physics »: Conference Series, 2014. Wind turbine industry utilizes composite materials in turbine blade structural designs because of their high strength/stiffness to weight ratio. T-joint is one of the design configurations of composite wind turbine blades. T-joints are prone to delaminations between skin/stiffener plies and debonds between skin-stiffener-filler interfaces. In this study, delamination/debond behavior of a co-bonded composite T-joint is investigated under 0° pull load condition by 2D finite element method. The failure sequence consists of debonding of filler/stringer interface during one load drop followed by a second drop in which the 2nd filler/stringer debonds, filler/skin debonding and skin delamination leading to total loss of load carrying capacity. This type of failure initiation has been observed widely in the literature. Failure initiation and propagation behavior, initial and max failure loads and stress fields are affected by the property change. In all cases mixed-mode crack tip loading is observed in the failure initiation and propagation stages. In this paper, the detailed delamination/debonding history in T-joints is predicted with cohesive elements for the first time.


 Read on
Read on